What do you mean by nutrition? The process by which animals consume food material by digesting, absorbing and assimilating the food material to grow the body, replenish waste and convert food energy into usable energy is called nutrition.
Importance and Significance of Nutrition
Nutrients serve various purposes in the body, such as:
(i) Growth and replenishment of the body – nutrition increases the dry weight of the protoplasm of the cell. As a result, the cell division is accelerated and the growth and decay of the body is completed.
(ii) Energy storage – Energy storage occurs in the organism through Kushti. When needed, the food stored energy is released and the tongue performs all the physiological activities. Such as movement, movement, excretion, birth etc.
(iii) Immunity – The immunity of our body is through nutrition.
(iv) Food storage- Nutrients store food in the body for the future so that when food becomes scarce in the future, the body uses that energy to meet its own needs. Food is stored mainly in the form of protein in plant bodies and in the form of glycogen and fat in animal bodies.
(v) Conservation of heat – Nutrition also plays a special role in the production and conservation of heat in the animal body.
What is food?(Nutrition)
The food which is consumed by the body for nutrition, growth, replenishment and supply of energy required for work and regulation of biological functions is called food. The things we eat are called arya materials. All food items are not food. All the aids that have the ability to produce overall energy are called food. The six components of food are – Carbohydrates, Proteins, Fats, Vitamins, Minerals and Water. So these three food ingredients are only food, other nutritional aids are not food. (Nutrition)
Why is food called a source of energy?(Nutrition)
It is the source of energy in living organisms. Food contains static energy, which is extracted from solar energy during photosynthesis. When food material is involved during respiration in living cells, the static energy is released as heat energy and controls all the biological functions in the living body. So food is the source of energy in the body. (Nutrition)
What are the types of food?(Nutrition)
Food can be mainly divided into three categories, namely – Carbohydrates or sugars, Proteins or meat, Fats or fats.
(i) Carbohydrates – organic compounds formed with the help of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen which help in the production of thermal energy.
2:1 ratio is called sugar or carbohydrate.
Source:-
Vegetable Sources- The main sources of carbohydrates are vegetable foods such as rice, wheat, maize, millet, potatoes, chickpeas, beets, carrots, dates, grapes, bananas, apples, bell peppers, watermelons, jaggery, sugar, gur, sweets etc.
Animal sources – Carbohydrates are very low in animal foods. Milk contains lactose and cow’s liver contains animal protein or glycogen.
Nutritional Importance in Human Body -(1) Carbohydrates increase body efficiency and produce heat energy. Combustion of 1 gm of carbohydrates produces 4.1kcal of heat energy. (2) Cellulose foods relieve constipation. (3) Glycogen is stored in liver cells. When blood glucose levels fall, glycogen converts to glucose and regulates blood glucose levels. (4) Protein helps in fat synthesis.
(ii) Proteins – Monomers of amino acids composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen helpers linked together by peptide bonds to form organic compounds are called proteins.
Source:-
Vegetable sources – Protein is found in pulses, wheat, soybeans, soybeans, beans etc.
Animal sources – Fish, meat, eggs, chickpeas, cheese etc. provide adequate protein.
Essential Amino Acids- Amino acids which are essential for growth and nutrition in the body but cannot be synthesized in the body, have to be taken from outside through food, are called essential amino acids.
For example, arginine, leucine, isoleucine, valine, lysine etc.
(iii) Fats or Lipids – Fatty acids and esters of glycerol composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen are called flats or lipids. Fats do not have a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen.
Vegetable sources – The mentioned fats are found in mustard, almonds, coconut, sesame, red beech etc.
Animal source – Animal fats are available in ghee, butter, fat etc.
Nutritional Importance of Fat – The main function of fat in the animal body is to produce its energy. 9.3 if 1gm of fat is burned
kcal heat energy is produced and vitamins A, B, E, K are kept dissolved and stored as fat in the animal’s body to regulate heat, serving as a future food source. (Nutrition)
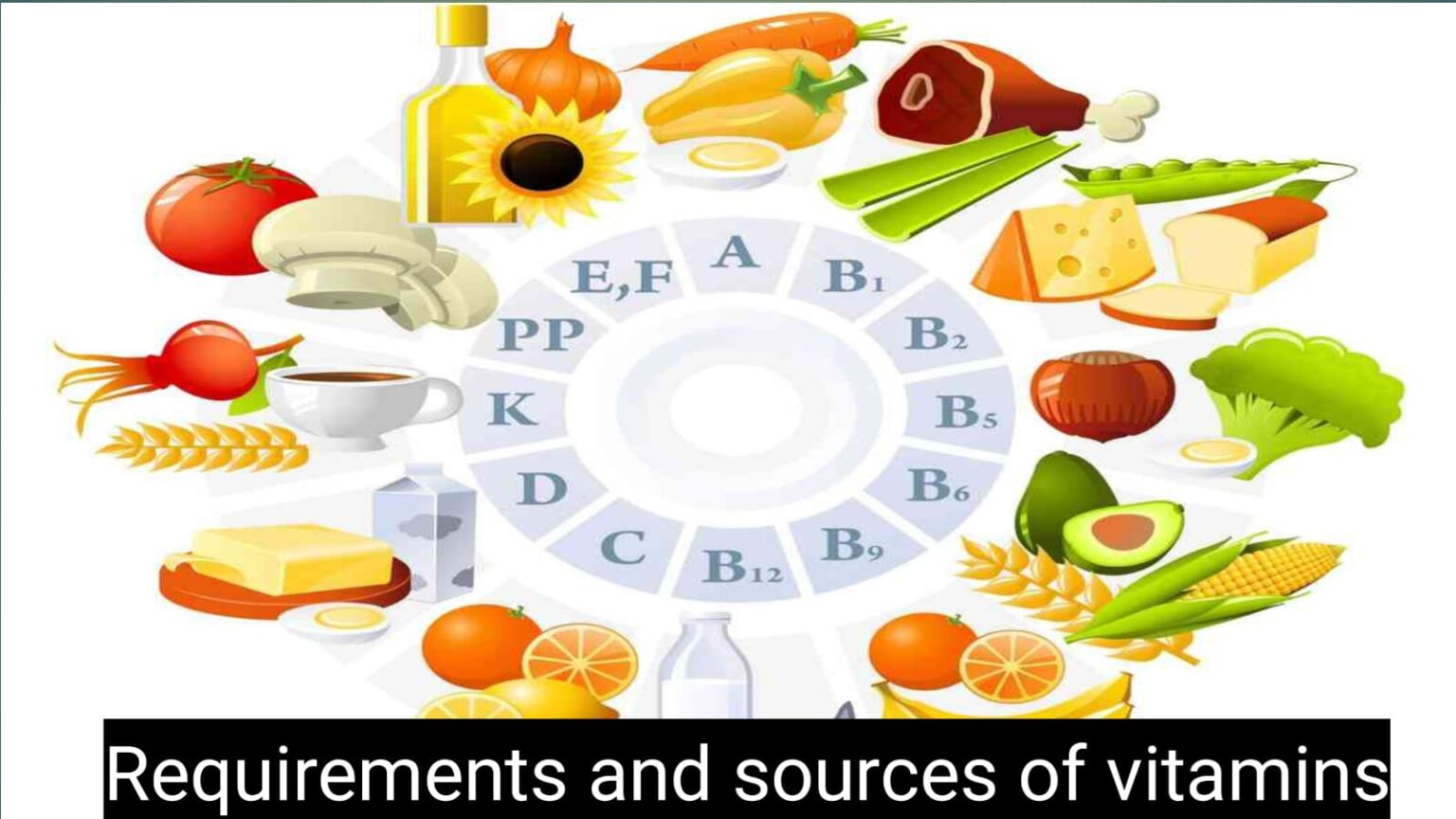
Vitamins or Food Life: (Nutrition)
Scientist Lunin first observed in 1881 that, despite taking all the necessary food, normal growth and nutrition of the organism does not occur in the absence of a particular food component. Scientist Hopkins is that kind of food
The material is termed as an ‘essential adjuvant food ingredient’. In 1911, scientist Kazimir Funk named this substance as vitamin. Later in 1920, Professor J. C. Drummond
Dropped the letter ‘e’ from ‘Vitamin’ and introduced the word ‘Vitamin’
Definition of Vitamin –
The special food component which helps in the normal nutrition and growth of the body from a small amount in the normal diet and increases the immune system and in the absence of which various disease symptoms appear in the body is called vitamin or food.
Importance of Vitamins –
Vitamins are very important in our body. Lack of various vitamins in our body can cause various diseases. For example, vitamin A deficiency can cause scurvy, vitamin C deficiency, rickets, vitamin E deficiency, beriberi, vitamin B-complex deficiency, mouth sores, anemia, sinus disease, etc.
Classification of Vitamins –
Vitamin K is divided into 2 parts according to solubility, viz.-1. Water-soluble vitamins, such as B-complex and C, 2. Oil-soluble vitamins, such as – vitamins A, D, E, K.
Vitamin-A :- Vitamin S is a soluble vitamin of new substances. The chemical name of this vitamin is retinol.
It also prevents xerophthalmia
It is called an anti-infective vitamin as it is anti-geriatric and prevents infection. This vitamin is synthesized in the liver from beta-carotene.
Source :- In the plant class this vitamin is found in orange colored vegetables such as carrots, tomatoes, ripe mangoes, spinach,
Found in cabbage, vegetable oil etc. And in animals it is the main source of oil secreted by the liver of fish like cod, halibut, shark etc. It is also found in milk, egg yolk, butter, fish etc.
Deficiency symptoms – The symptoms that are manifested due to lack of vitamin A are – the normal growth of the body is disturbed, the rhodopsin synthesis of the retinal rod cells is disturbed due to the lack of vitamin A, the symptoms of night blindness are manifested, besides the dry supply of the retina or serophthalmia i.e. blindness symptoms are seen, the eyeballs Destruction and cataracts, spots on the conjunctiva, destruction of the lining of the ureter and formation of ring stones, abnormal overgrowth of the spine and crown.
The main function of vitamin A is to help the growth of the body, to synthesize road coaching in the rod cells of the retina, to maintain the normal activity of the G or pharyngeal system and the secretory organs of the salivary glands, to prevent infection, to help in normal growth.
Vitamin B:- Vitamin B-complex is a combination of many vitamins, these are respectively -Vitamin B1,Vitamin B2,Vitamin B3,Vitamin B5,Vitamin B
B6, Vitamin B12, Vitamin H, Kaling etc.
Vitamin B-complex is a water-soluble vitamin.
Source :- In plant body it is found in brown rice, red flour, yeast, rice bran, almonds, cabbage, spinach, tomato, sprouted gram etc. And in the animal body it is found in milk, eggs, goat liver, fish, meat etc.
Deficiency symptoms:- Deficiency of vitamin B causes beriberi disease, the symptoms of this disease appear in the limbs. Also deficiency of this vitamin can cause sore lips and sore tongue.
Vitamin C:- The chemical name of vitamin C is ascorbic acid. It is said that vitamin C prevents Kavi
Called anti-car beautic vitamins. It is a water soluble vitamin Vitamin C is destroyed by cooking.
Source – Vitamin C is found in all types of fresh fruits especially sour fruits. For example, oranges, lemons, tomatoes, amlaki, pineapples and in animals it is present only in breast milk and in small amounts in fish and meat.
Deficiency Symptoms – The major deficiency symptom of this vitamin is scurvy.
Vitamin D:- Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin. Its chemical name is calciferol.
This vitamin is synthesized from ergosterol in the skin with the help of ultraviolet rays from sunlight.
Sources – Vitamin D is found very sparingly in plants. This vitamin is found in small amounts in vegetable oils and in animal bodies it is found in large amounts in fish liver extract. It is also found in milk, eggs and butter.
Deficiency symptoms – Deficiency of this vitamin leads to low calcium levels in the blood due to excessive excretion of calcium and phosphate in the stool. The result is rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.
Vitamin E:- Vitamin is a fat soluble vitamin. Its chemical name is tocopherol. This vitamin prevents infertility and is called antisterility vitamin.
Sources – Various vegetables, sprouted chickpeas, beans, soybeans, wheat contain this vitamin but animals contain very little of this vitamin. This vitamin is found in milk, meat, egg yolk etc.
Deficiency Symptoms – Deficiency of this vitamin causes decreased fertility in women resulting in infertility.
Vitamin K:- Vitamin K is a fat soluble vitamin. Its chemical name is phylloquinone or naphthoquinone.
Sources – In plants this vitamin is found in cabbage, spinach, soybeans, tomatoes etc. and in animals this vitamin is found in cow and pig liver and milk and eggs.
Deficiency symptoms – Deficiency of this vitamin results in reduced blood levels resulting in bleeding or hemorrhagic symptoms. (Nutrition)